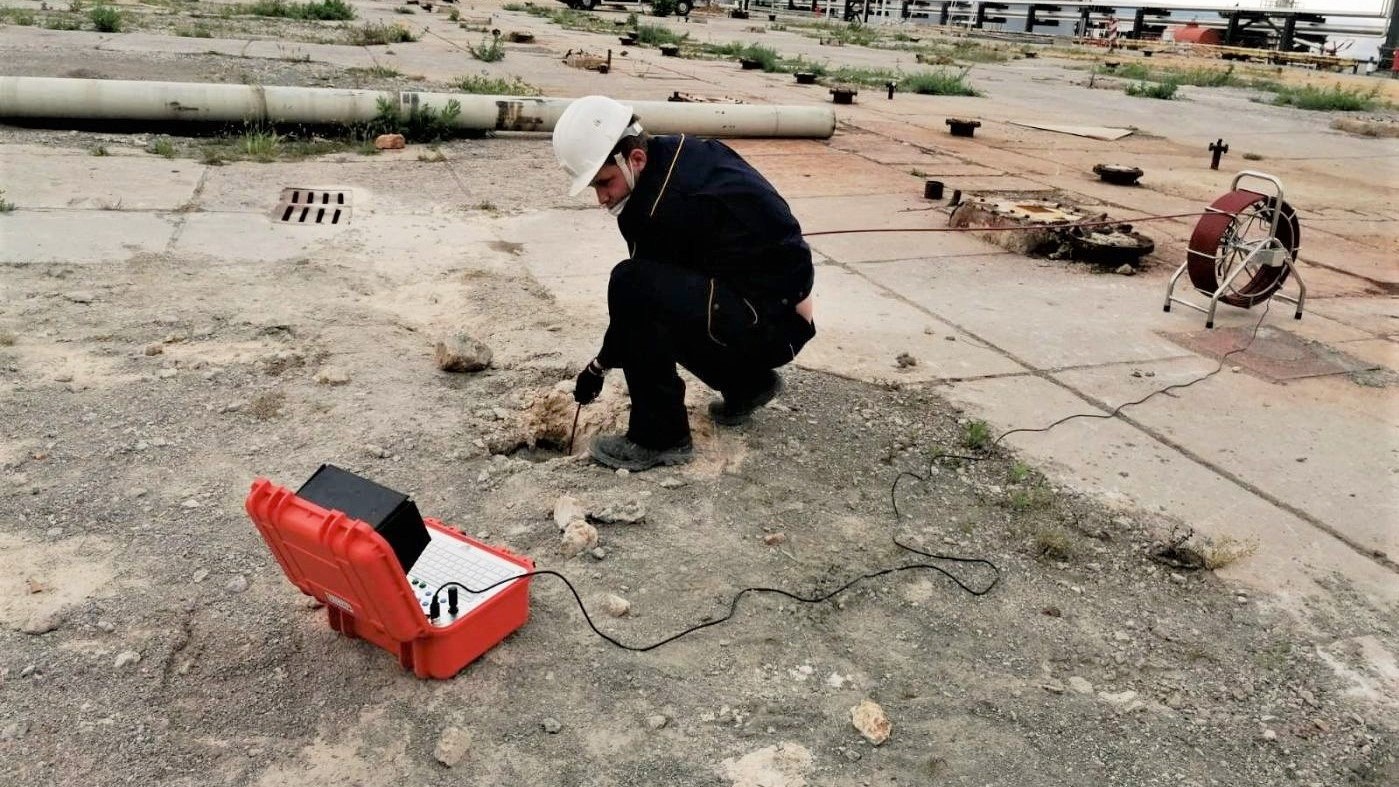
Video logging in boreholes
For the purpose of design, construction and management of large hydrotechnical and geotechnical structures, there was a need for an instrument adapted for use in the karst area. Based on experience with the application and servicing of existing instruments, activities related to their improvement as well as the design of a new hydrogeological instrument for technical video logging adapted for use in our karst areas began in the mid-80s.
Technical video logging is the technique of conducting visual logging within buildings and structures. In designing the video logging instrument, the need for quality frame registration and precise determination of video camera position in space as well as the details in its field of vision in the most complex field conditions were taken into account.
Video logging in boreholes
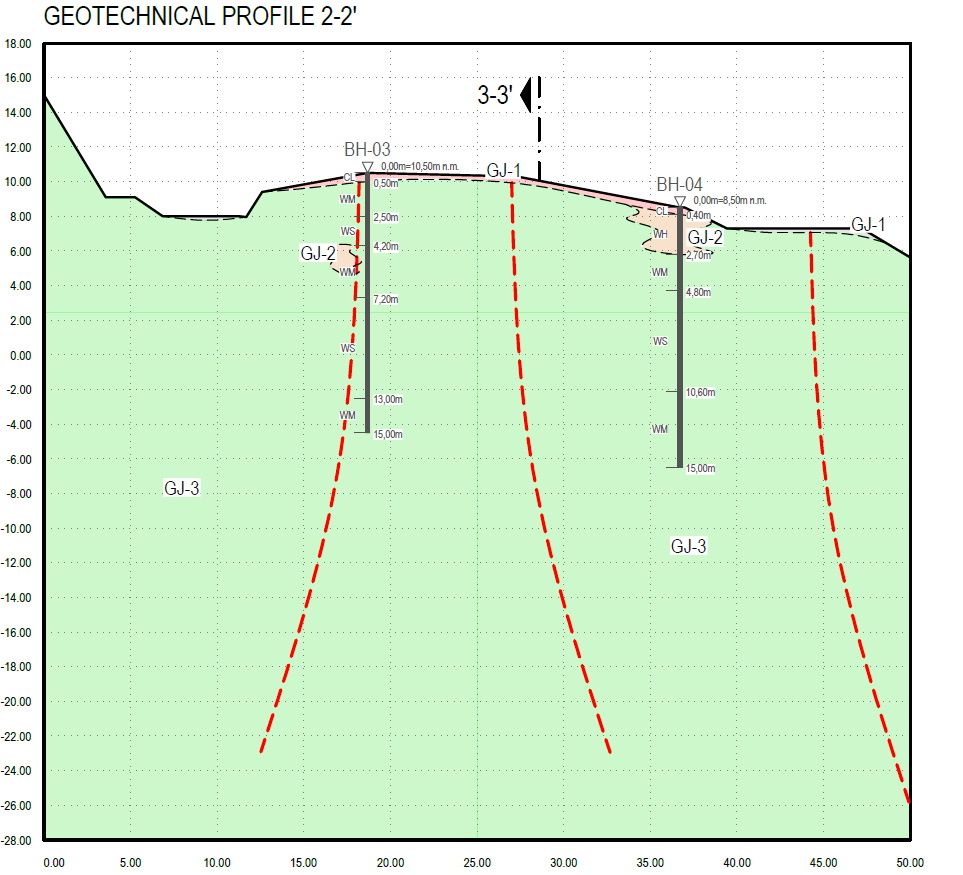
Video logging in boreholes is carried out after exploratory drilling. Using a “lateral” camera (vertical and horizontal recording) and a “push-rod” camera (vertical recording), underground and/or underwater phenomena and processes resulting from natural substrate are recorded. The cameras provide a continuous, oriented, 360° optical image of the original (natural) colors along the walls of the borehole.
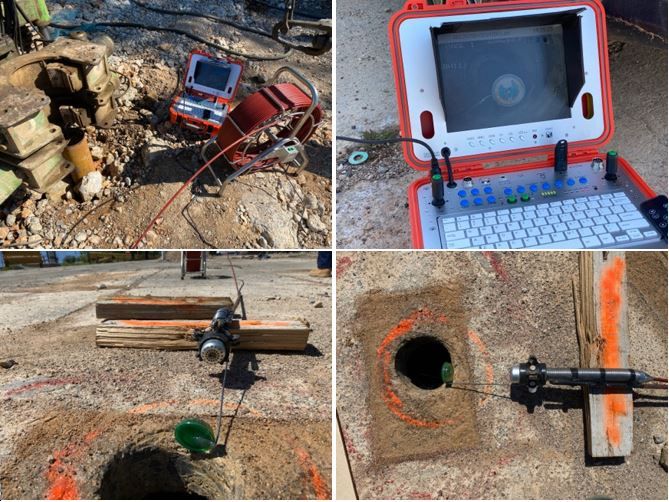


The equipment consists of three main parts: the camera head, the cable drum and the control station. Although complex investigation is carried out on both substrates and structures in the design, construction and operation of hydrotechnical and geotechnical structures and artificial lakes, it is impossible to completely rule out unforeseen situations or accidents. Therefore, video logging gives us insight into underground behavior and can be of great benefit.
A video logging record contains:
- video of the entire borehole,
- accompanying photos of the borehole taken during borehole logging,
- orientation display using a compass needle along the entire drilled borehole,
- depth (measured in meters),
- borehole mark, so that it is possible to distinguish different boreholes,
- time and date stamp.
With the obtained data, better engineering geological interpretation becomes possible, made even more precise by information such as layers and depths of the soil foundation, surface discontinuity spacing, discontinuity separation, discontinuity fracture filling, roughness and discontinuity orientation.
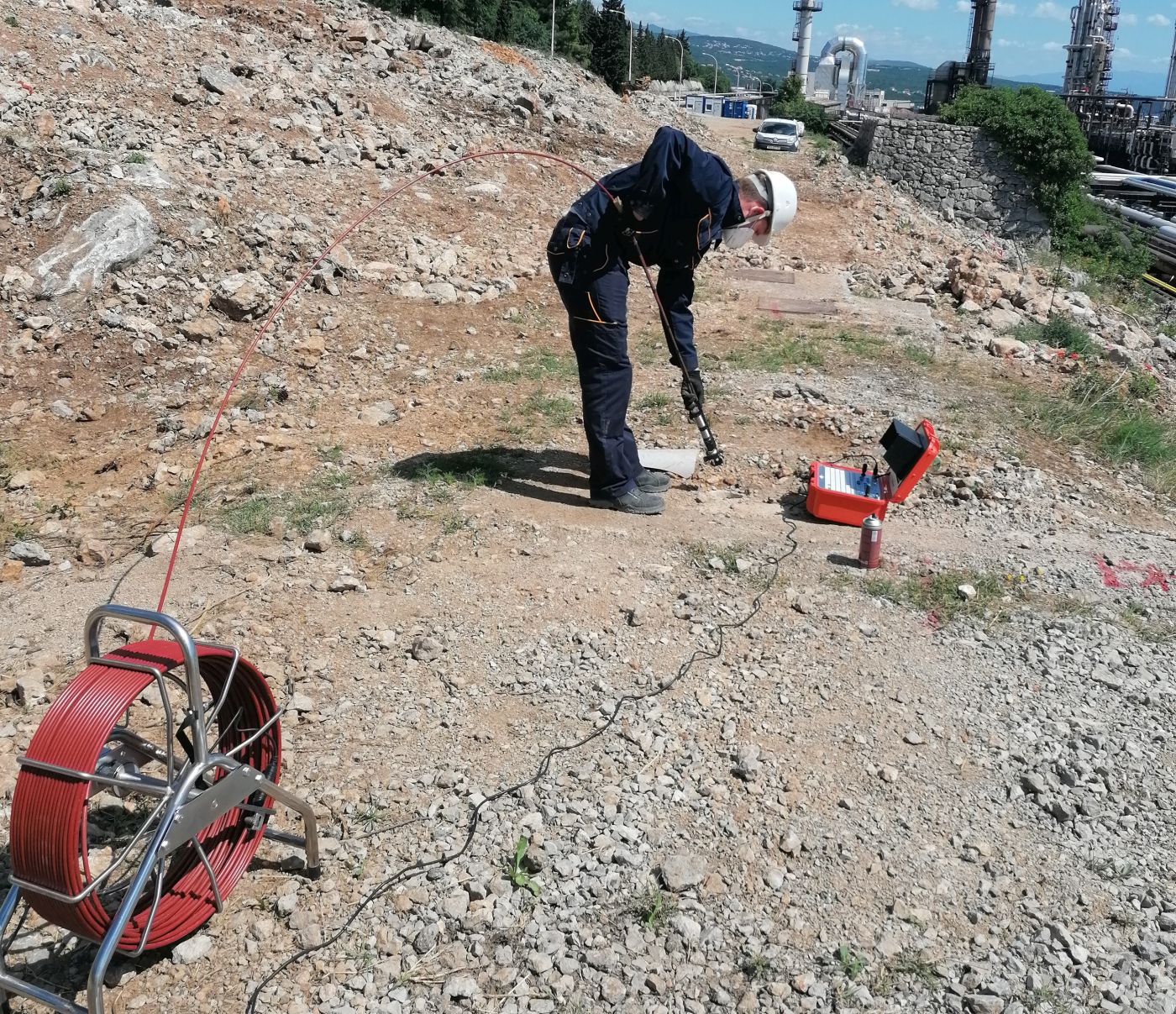

During video logging observations in old and new piezometric and hydrogeological exploration boreholes on the karst coast, a large amount of digital video information was collected. Technical data of exceptional precision was obtained by their sophisticated computer processing, on the basis of which the geological, hydrogeological and geotechnical interpretation of the investigated area was supplemented. This has greatly expanded the results of previous investigations in this area. The underground flow in piezometric boreholes (where the hydrodynamics of underground flow was investigated) and the water/sea level in the exploration boreholes were also determined using video logging.
Photos 8-11 were taken in boreholes and were used to make the attachments shown in photo 12.
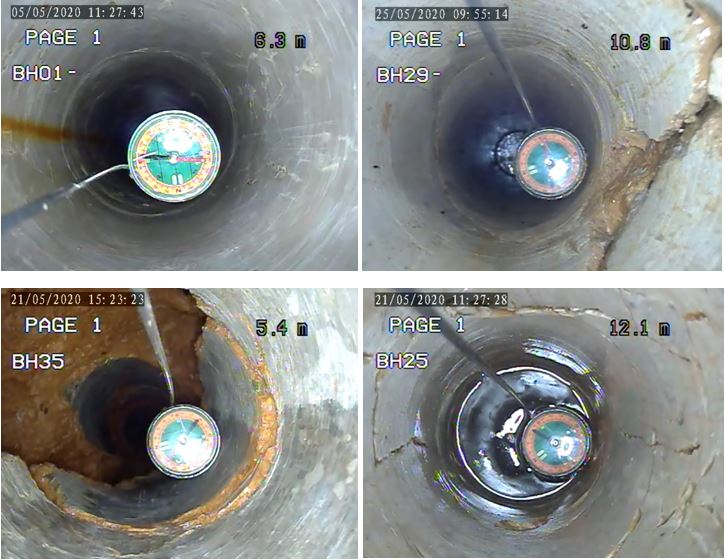

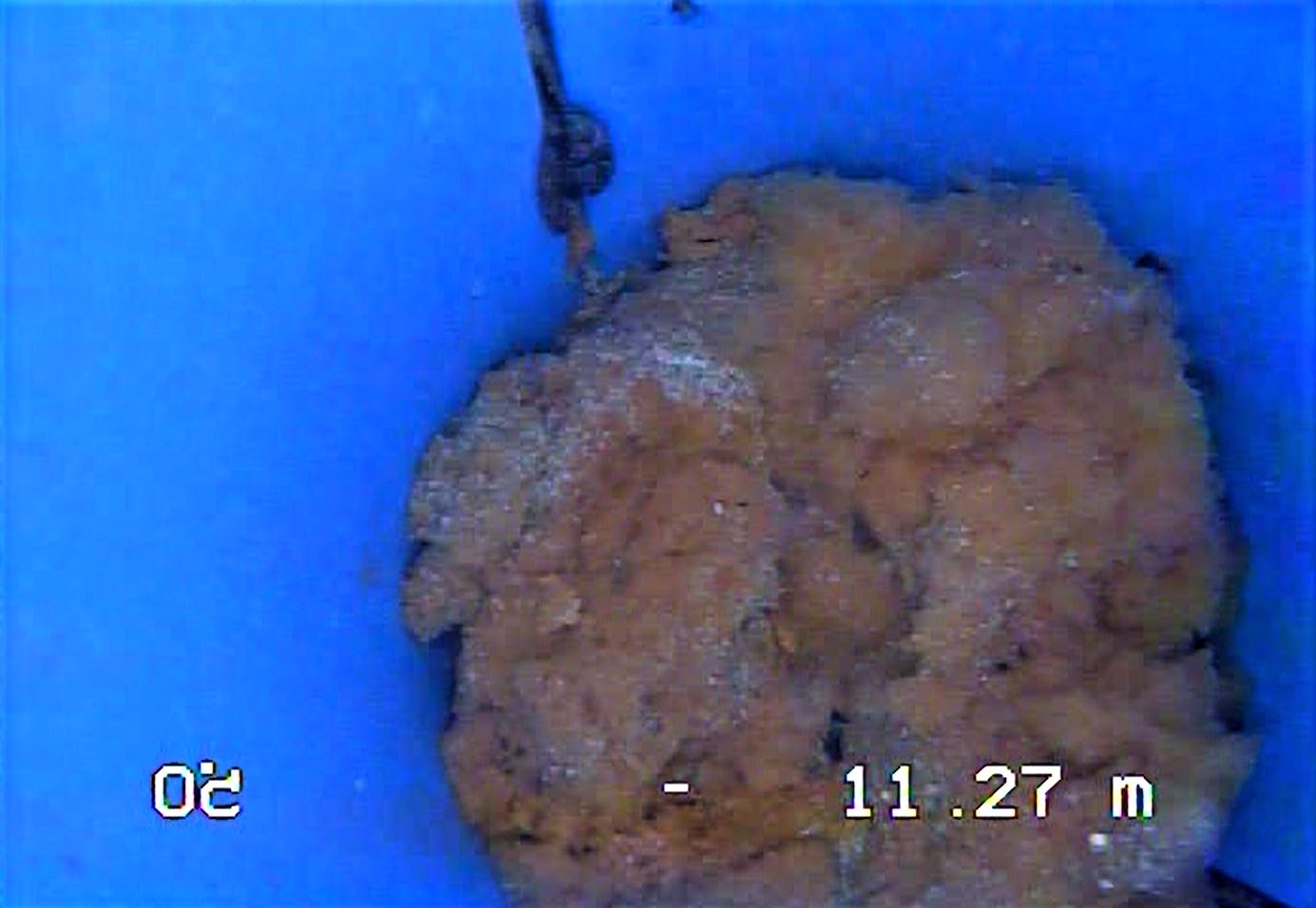
Video logging can also be carried out when prospecting the physical condition of existing wells. Based on the recording, the condition of the well in which it is currently located is defined, i.e. if there have been certain changes or damage to the well structure in relation to the constructed condition. Picture 13 shows a recording by a video logging in an existing well with a depth of 25.0 m. The picture shows a layer of brownish-yellow color at the bottom of the structure. It is a layer of bacteria on which sand has been deposited, which creates a “plug” at the bottom of the structure and thus prevents the normal functioning of the well. During sampling, and due to poor installation of the pump, sand was pulled in, which created a seal in the construction – a “plug”. There are free iron atoms in the water which, in combination with oxygen, create bacteria that settle in the structure.

Conclusion
The results of application so far show the importance of video logging in little-known and hard-to-reach places, primarily underground and underwater. By combining the method of technical video logging with other technical methods for examinations and observations, the investigation and testing is rationalized and a better interpretation of the overall investigated results is achieved. The method of technical video logging could join other standardized investigative methods in the design, construction, maintenance and control of general technical safety of engineering structures.
Read more: How to determine number and depth of exploration boreholes, INA Rijeka Refinery Modernization Project
