Geophysical surveys
Geophysical surveys are performed from the soil surface, through boreholes, excavations or in a combination of placing sources and detectors. The survey scope, the method types
Geophysical surveys can offer significant time and economic savings and provide data on a much larger volume of soil or rock mass compared to conventional soil and rock mass survey.
Generally, we distinguish between the following geophysical methods:
- electromagnetic methods
- magnetic methods
- seismic methods
- electrical methods
georadar
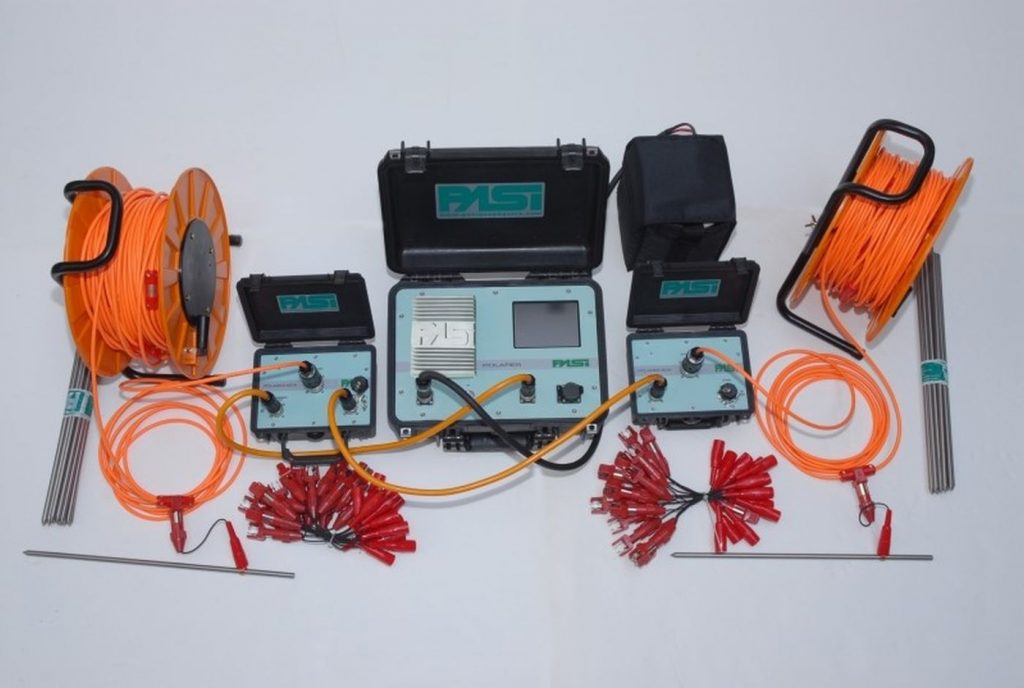

The description of commonly used geophysical methods in geotechnical engineering is shown below.
Seismic refraction
Seismic refraction is based on measuring the propagation time of elastic seismic waves, from sources to geophones, through subsurface geological structures. The waves bounce and break at the material boundaries of different densities and deformation properties.
A seismic wave is generated on the surface by striking a hammer or a vibrator. The wave arrival on the surface is detected by measuring sensors – geophones.
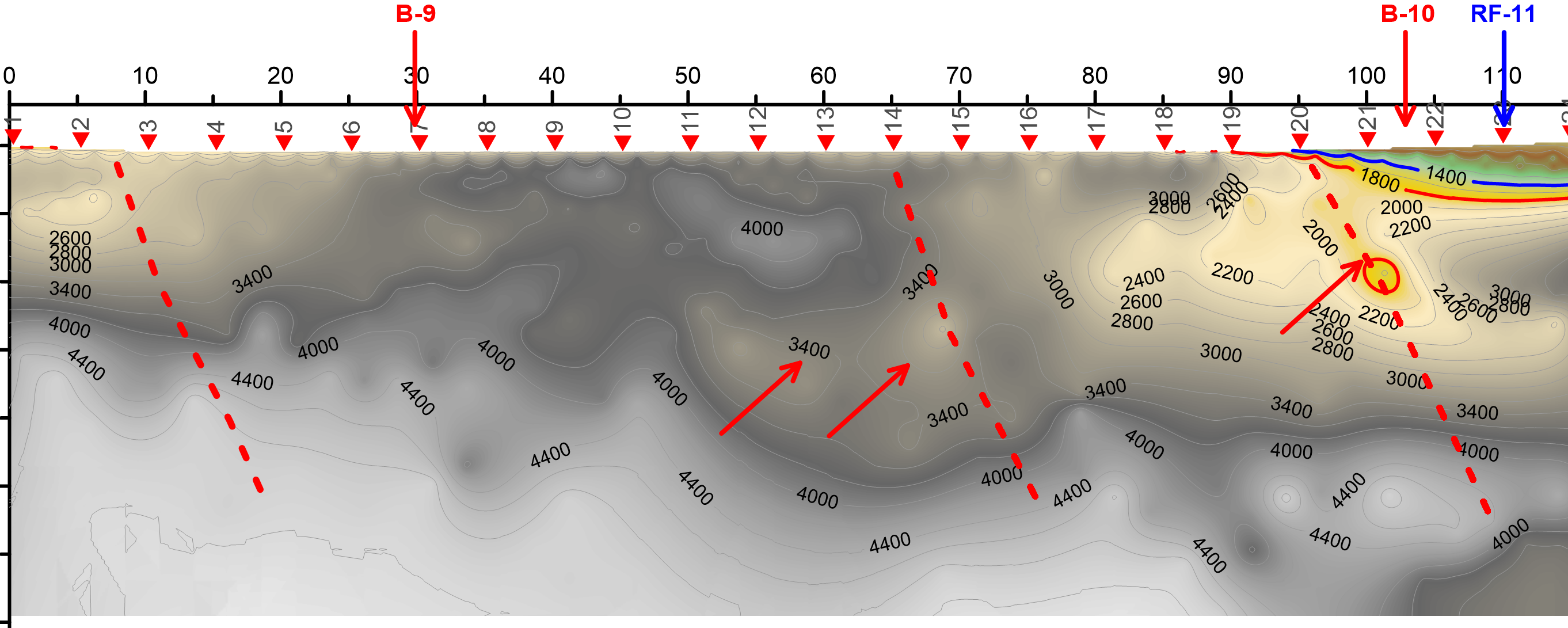
Seismic refraction measures the wave time traveling from a source to a layer of varying density,
Seismic refraction is used when shallower depths of soil foundation are analyzed and for determining wear zones.
Seismic reflection
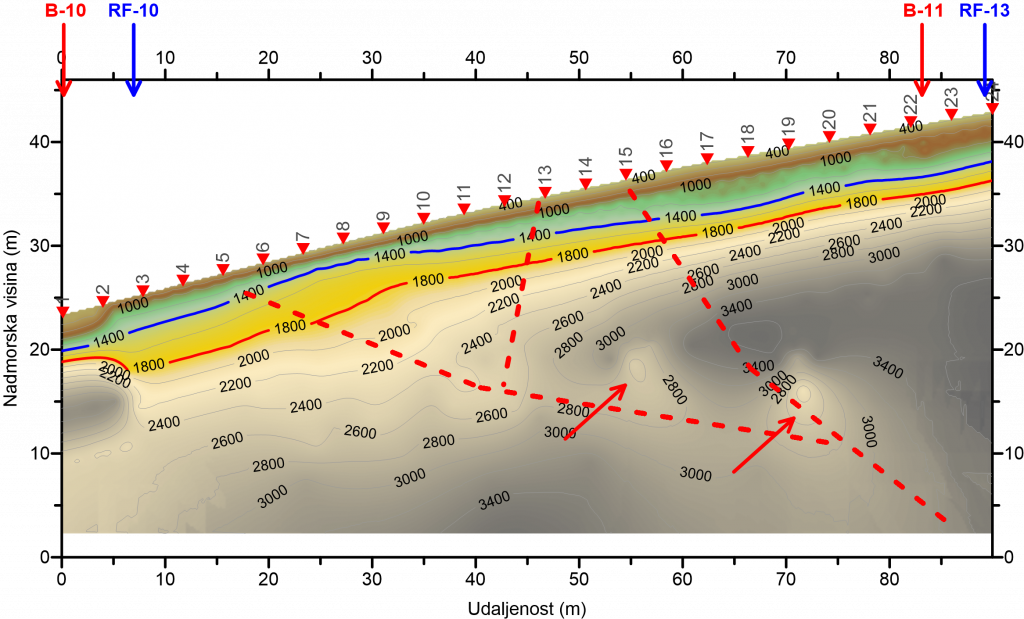
Seismic reflection, as well as seismic refraction, is based on measuring the propagation time of elastic seismic waves. The difference between these two methods is that seismic reflection measures the time of a seismic wave that is approximately vertically reflected on a surface of different density and travels to the geophone. The generation of a seismic wave is the same as that of seismic refraction.
Seismic reflection is used when greater depths of soil foundation are analyzed and for determining faults and caverns.
SASW
Spectral analysis of surface waves (SASW) is a seismic method developed to determine elastic modules of various materials and to change these modules with depth.
The method is based on waves characteristics moving along the terrain surface, in the vertical and horizontal directions, and causing circular motion of soil particles.
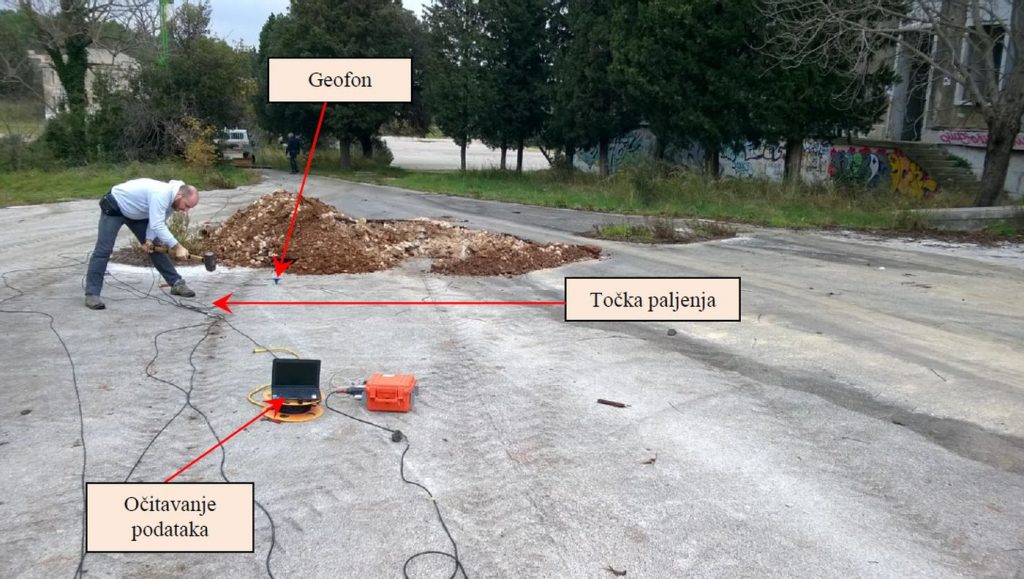
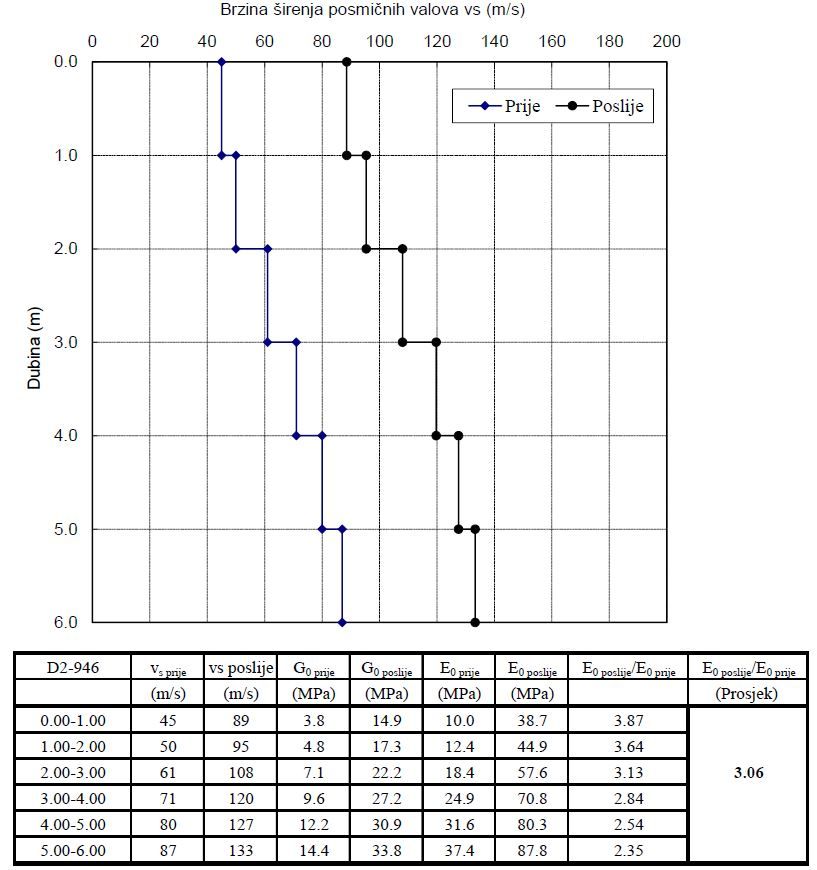
The wave source can be a rotating mass oscillator or some other source of a dynamic strike that causes oscillations. Waves are detected by geophones placed on the terrain surface that measure the arrival time of the wave. From the frequency of the oscillator and the time of wave occurrence, a profile of the velocity of shear waves in the soil is obtained. It is used to determine the profile of soil stiffness by depth.
The SASW method is mainly used for verification of projected soil improvement. The SASW test is performed before and after the soil improvement is planned. By comparing the obtained stiffness profiles in depth, the average degree of improvement performed is obtained.
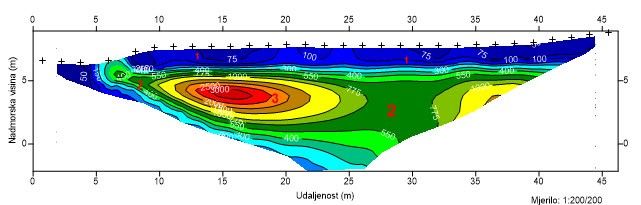
Geoelec tric tomography
Geoelectric tomography is a method based on the determination of different electrical resistance of different types of rocks and materials that indicate differences in the geological terrain structure.
The method uses current that is released into the foundation soil by electrodes, resulting in a potential field in the foundation soil. The generated field is measured by the second pair of electrodes. Changing the electrode depth and their distance, horizontal and vertical distribution of potentials or apparent resistance of the foundation soil is obtained.
The data obtained by measuring apparent resistances for each electrode position are shown in the form of a two-dimensional cross-section of apparent resistances. Pseudosection is a section of the underground that is obtained by plotting apparent resistances just below the middle of the electrode arrangement at a depth proportional to the electrode distance. By interpreting the
The advantage of geoelectric tomography is fast testing performance and obtaining a large number of measuring data.
Conclusion
Geophysical surveys have many advantages, primarily in terms of time saving and economic resources. Instruments are relatively cheap, and exploration is much faster and cheaper than conventional geotechnical exploration and investigation – exploratory drilling. Proper selection of geophysical survey accelerates and improves exploration, which reduces the exploratory drilling scope as an expensive and demanding research method.
Read more: SASW