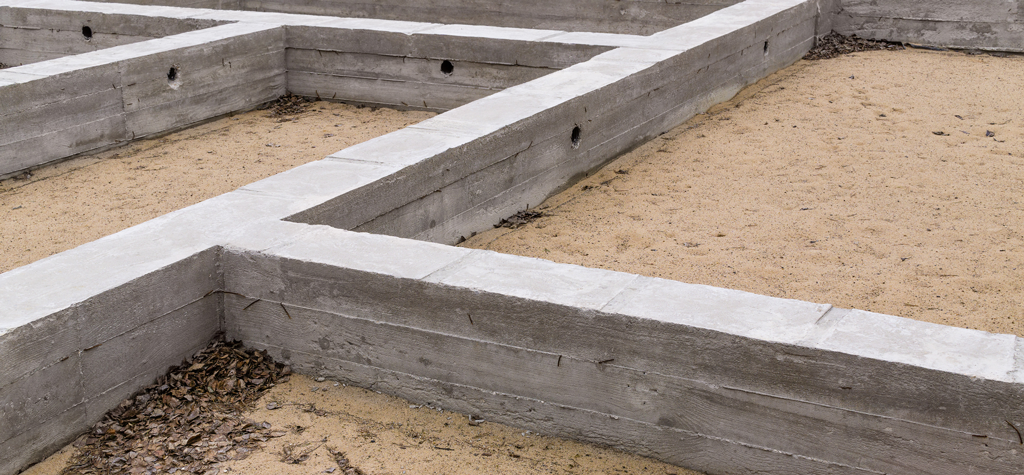
Types of shallow foundations
Shallow foundation
Foundation depth usually involves depth, measured from the terrain surface, to the base surface through which the foundation transfers the structure load to the soil. According to Eurocode, shallow foundations are considered to be bases whose width is greater than the depth of foundation (D <B). Shallow foundation is applied in cases where the good load-bearing soil is at a relatively low depth.
The foundation depth must meet the safety requirements of the breakdown, whereby after the load application, the complete structure settlement will be within acceptable limits. Foundation depth is also conditioned by local climate conditions. The minimum value depends on the depth of the freezing soil, which is defined by the lowest temperature in the shade for the return period of 50 years. During soil freezing, the water is attracted to the frozen area from a greater depth so the foundation cavity must be below the freezing depth.
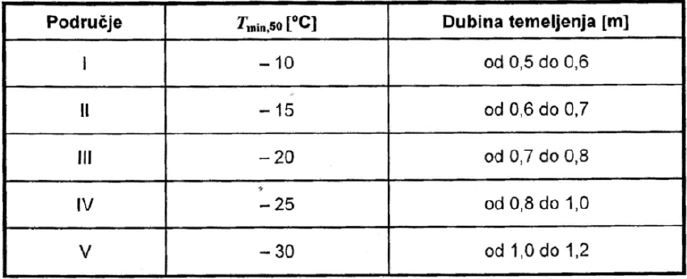
(for the 50-year return period)
Types of shallow foundations
Shallow foundations can be divided into:
- Spread footings
- Strip footings
- Slab foundations
- Grid foundations
Spread footings
Spread footings are types of shallow foundation
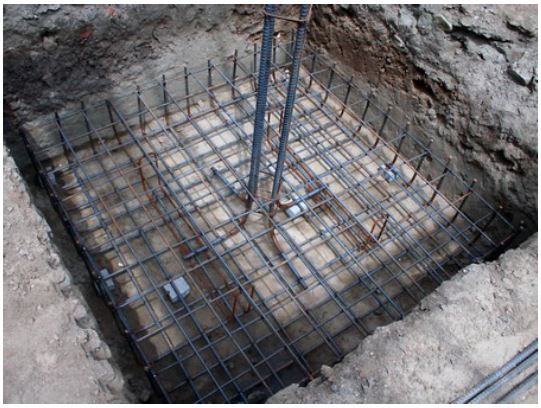
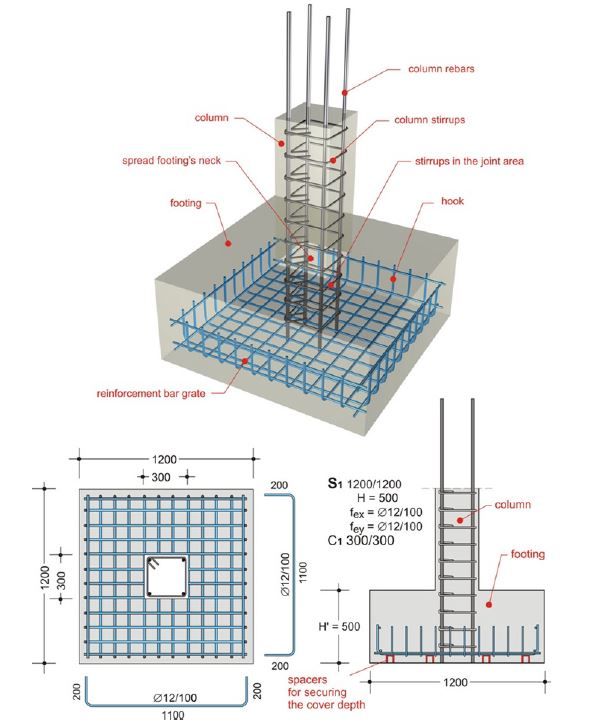

The spread foundations according to their stiffness can be divided into solid and flexible foundations. The relation of soil stiffness and foundation defines the deformation and distribution of strain at the contact of the foundation and soil. The criterion for determination of spread foundation stiffness depends on the soil foundation reactor module and is valid for K> 0,40 for solid foundations, i.e. K <0,40 for flexible foundations.
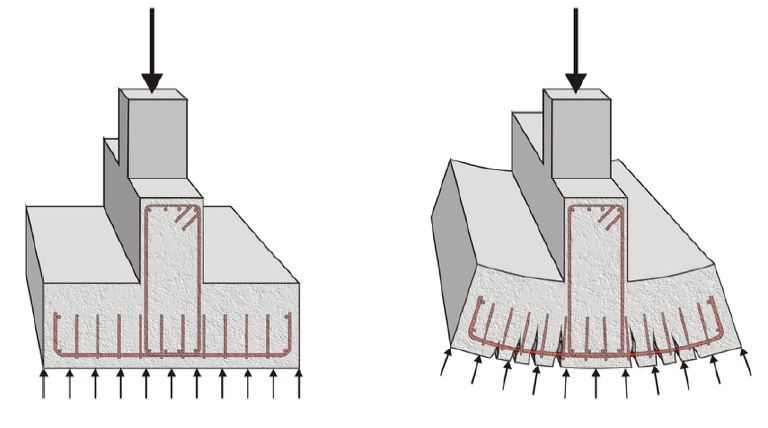
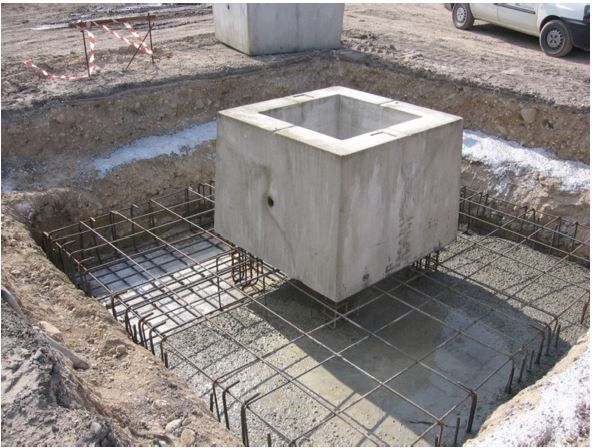
Because of the required construction speed, the prefabricated spread foundations on the prepared substrate are often used. The compound of the prefabricated foundation and the future structure is carried out by filling the micro-concrete.

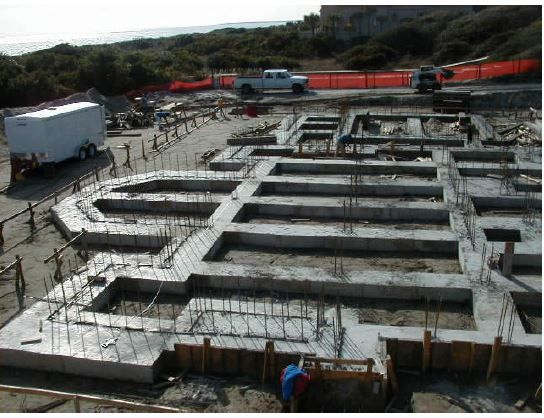
Strip footings
Strip footings are performed underneath a series of columns or supporting walls and in case the strain on soil foundation underneath the spread foundation is large. Strip footings also prevent the horizontal distortion of individual foundations and strengthen them. In the longitudinal direction, the strip footings act as a continuous carrier under the force influence from the columns/walls.

Slab foundations
Slab foundations are shallow foundation structures placed underneath the entire structure in the following cases:
– If the spread/strip foundations would be too close to each other.
– For the foundation of tall structures and those with high loads (industrial facilities, warehouses).
– For resolving differential settlement issues (soil foundation of different strength and deformability characteristics).
The slab foundations are reinforced as two-way load-bearing plates with a

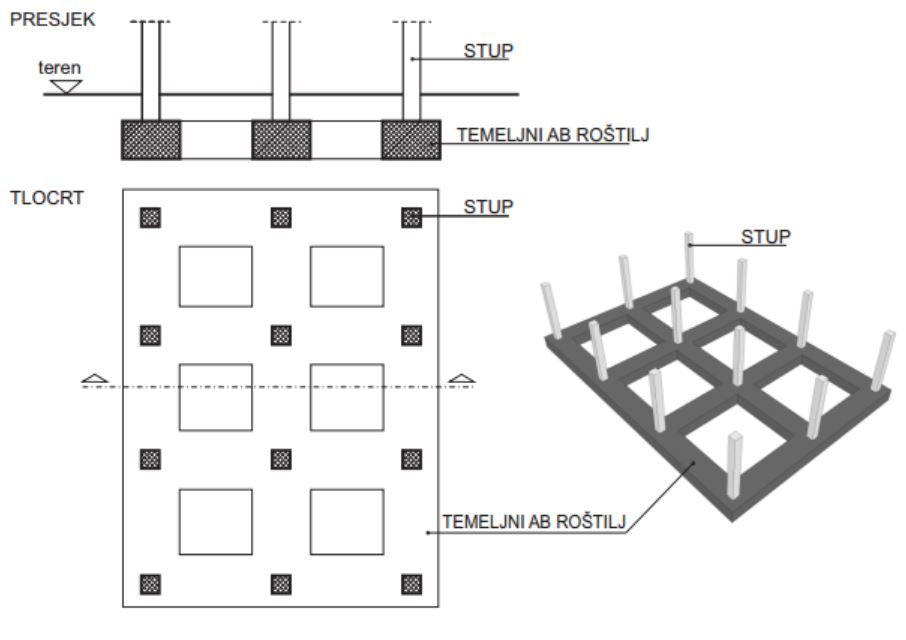
Grid foundation
The grid foundation is made up of interconnected strip foundation. This type of shallow foundation is appropriate when the columns extend in two directions in an approximately square raster and the foundation beams can be made in two orthogonal directions forming a grid foundation. This ensures a large contact surface and a good connection of the structure in both directions.
Shallow foundation is considerably more cost-effective than deep foundation. It should be applied where appropriate measures and procedures can achieve the required structure reliability in terms of the end-of-bound state (soil breakdown under the foundation) and the limit state of usability (permitted settlements).
Read more: Foundation remediation, Material replacement under foundation
