Pile integrity test
What is pile integrity test?
Pile integrity test covers the procedure for determining the integrity of individual vertical or inclined piles by measuring and analyzing the velocity (required) and force (optional) response of the pile induced by an (hand held hammer or other similar type) impact device usually applied axially and perpendicularly to the pile head surface.
Pile integrity test (PIT), or as ASTM D5882 refers to it as low strain impact integrity test, is a common non-destructive test method for the evaluation of pile integrity and/or pile length. Pile integrity test can be used for forensic evaluations on existing piles or quality assurance in the new construction.
Low strain impact integrity testing provides acceleration or velocity and force (optional) data on slender structural elements (structural columns, driven concrete piles, cast in place concrete piles, concrete filled steel pipe piles, timber piles, etc.).
The method works best on solid concrete sections, and has limited application to unfilled steel pipe piles and H piles. The test results can be used for evaluation of the pile cross-sectional area and length, the pile integrity and continuity, as well as consistency of the pile material. This evaluation practice is approximate and provides a rapid and simple way for evaluation of a large number of piles in a single working day.
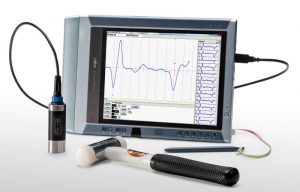
Photo 1. Equipment for pile integrity test
How to perform pile integrity test?
The pile head surface should be accessible, above water, and clean of loose concrete, soil or other foreign materials. Any type of contamination should be removed (using a grinder) to reach sound concrete surface. This step is so vital, because the sensor and concrete should in firm contact.
The location of the sensor should be away from the edges of the pile. The integrity testing should be performed no sooner than 7 days after casting of concrete.
A hammer is used for impacting pile top. Motion transducer should be capable of detecting and recording the reflected echos over the pile top. Acceleration, velocity, or displacement transducers can be used for this purpose. The distance between the impact location and the sensor should be no larger than 300 mm. Several impacts are applied to the top of the pile. The reflected echos are then recorded for each individual impact.
The primary shock wave which travels down the length of the pile is reflected from the toe by change in density between the concrete and the subsoil. However, if the pile has any defects or discontinuities within its length these will set up secondary reflections which will be added to the return signal.
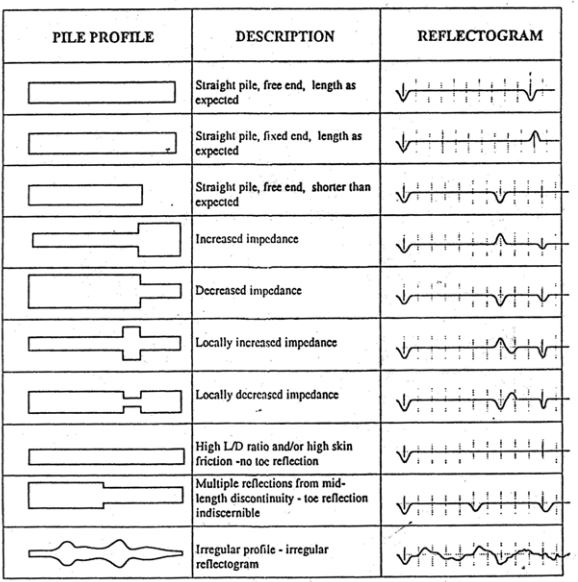
Photo 2. Typical reflectograms
What information does pile integrity test provide?
The Pile integrity test provides information about:
- Continuity of pile
- Defects such as cracks
- Necking
- Changes in cross section
- Approximate pile lengths (unless the pile is very long or the skin friction is too high).
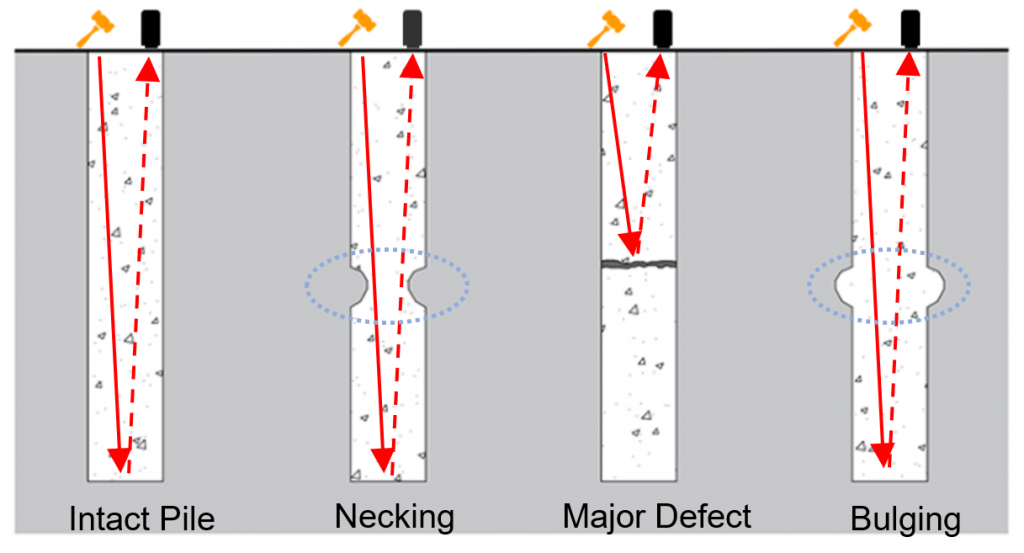
Photo 3. Pile integrity test – pile defects
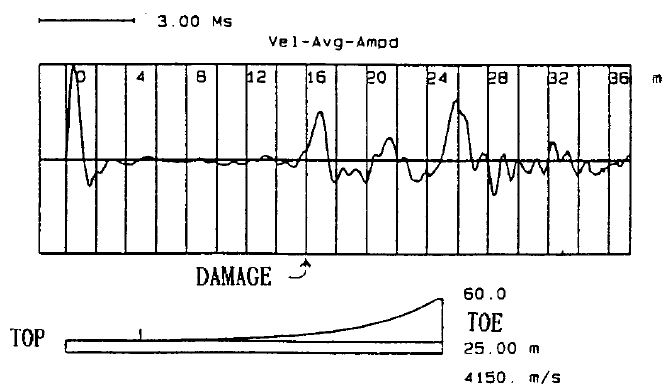
Photo 4. Typical velocity record indicating severe damage or cracked pile
Limitations of pile integrity test
Pile integrity test provides an indication of soundness of concrete, however the test has certain limitations:
- Pile integrity test can not be used over pile caps.
- It does not provide information regarding the pile bearing capacity.
- Test should be undertaken by persons experienced in the method and capable of interpreting the results.
- This test is not effective in piles with highly variable cross sections
- It is not effective in evaluating sections of piles below cracks that crosses the entire cross sectional area of the pile.
