GIS system application in business planning
Regardless of the type of data, objects and activities one is working with, the easiest way to manage and organize them is by using a system. In the case of business and spatial planning, the most useful is the geographic information system, or GIS.
Although all systems involve connecting activities and objects that serve a particular common purpose, the GIS is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. The system includes the necessary programs and a spatial database (Rhind&Mounsey, 1989).
GIS software and QGIS
Because of their extreme complexity, geographic information systems are considered to be one of the most complex and most extensive areas of computer application nowadays. They were built to encompass the entire space of the Earth, as well as to successfully manage all its aspects, combining geology, traffic, meteorology, forestry, ecology, water management, agriculture, oceanography and IT disciplines, such as database design and automatic data collection.
QGIS is a free GIS, an open source user-friendly tool. Launched by volunteers, the application is developed in the programming language C ++. This tool is able to manage, edit, analyze and visualize data on a map, and it also lets you create your own maps. QGIS plugins are used do expand the existing capabilities and functionalities, such as downloading points, paths from GPS devices, displaying layers using WMS, WFS, and OGC standards, or entering data using delimited text.
The figure below shows an overview of our database in the Republic of Croatia created with QGIS software:
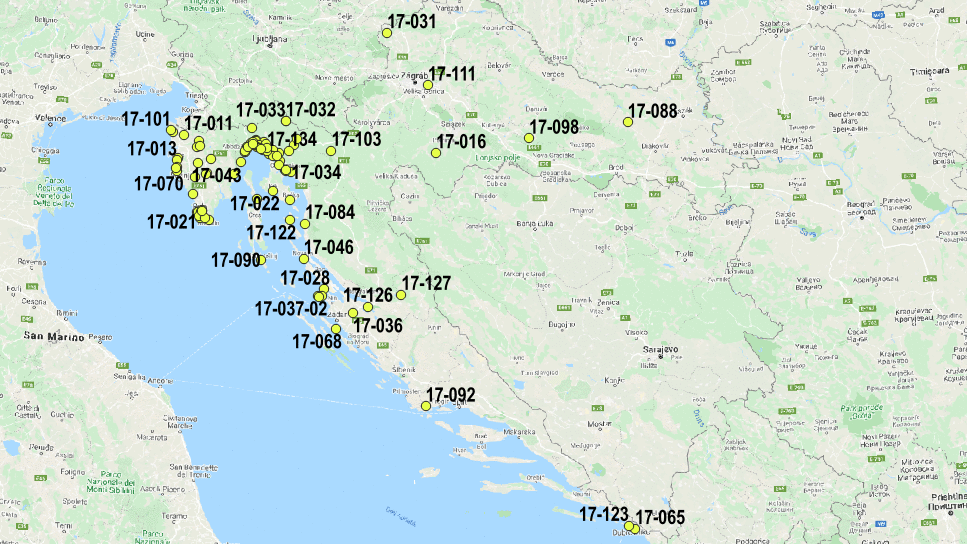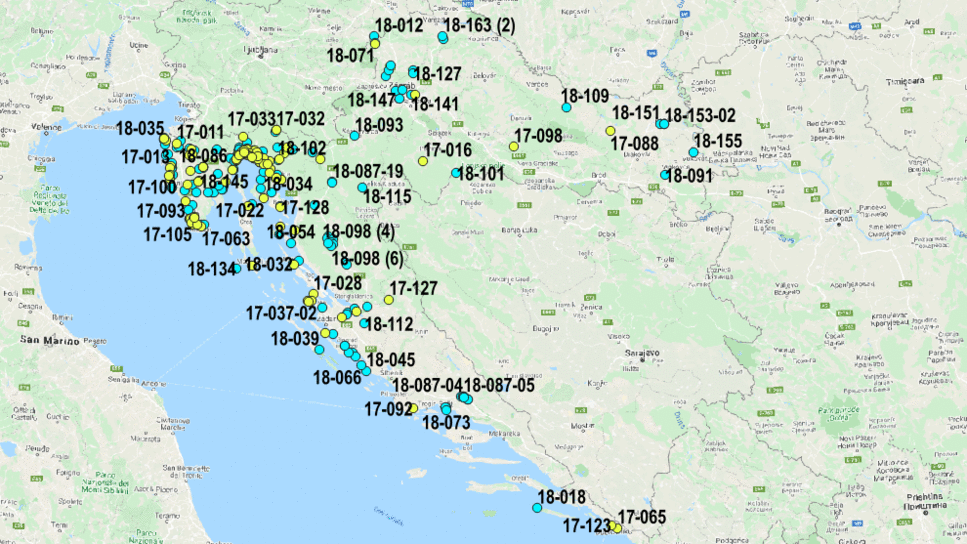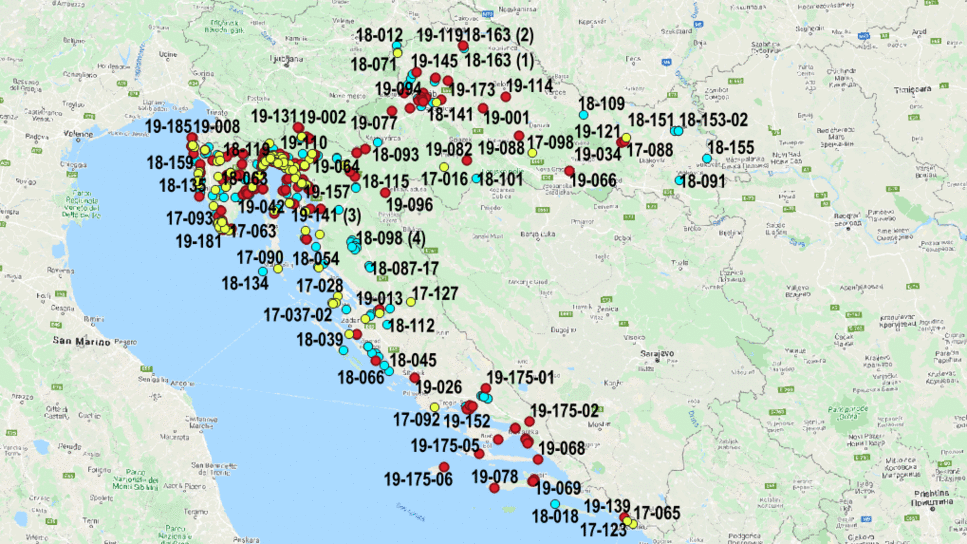
GIS application in geotechnics
Using the open source QGIS tool, we have created an overview of our projects over the past 10 years in the business. The factors taken into consideration were georeferenced Basic Geological Maps of the Republic of Croatia, WMS maps and flood risk and hazard maps. When overlapping maps, the most important element of GIS is data, and each piece of data has its own special characteristics. When adding layers (overlapping maps), we used work orders that provide a position for the data directly and indirectly and display it graphically. Maps were used as the source (base) data. The spatial component includes spatial attributes – latitude, longitude, height and other data that define the location of a work order.
In addition to the spatial component, the information component (names, descriptions, functions and other characteristics of a work order at a specific location) is extremely important, because it completes the data and makes them practical and useful. All spatial data can be reduced to three basic elements – points, lines, and polygons. Even though they may be in different forms, the basic two forms are raster and vector. We presented the spatial data in vector form, and the points, lines and areas information was coded and stored in a digital coordinate system. The work order on the map is indicated by a point (in vector form as the x, y coordinate of the point). It is also possible to add topology to such data (to determine relationships between geometries), and the shape itself can be used to store geodetic survey data or to digitize existing ones.
This system is multifunctional specifically because it can be expanded at any time in accordance with user needs in the sense of dedicated software solutions. It makes it possible to maintain a complete record of the business, and it is also an excellent basis for the further development and upgrade of the system. Maintenance is a continuous and changing process with new spatial and attribute data constantly appearing and changing the state of the geoinformation system.
An example of using GIS software in geotechnics:
Conclusion
Like any other information program, GIS has its advantages and disadvantages. The most significant advantages are the connecting of attribute and geographical features, data visualization and the possibility of interdisciplinary decision making. At the same time, some disadvantages should be mentioned, one of them being the time it takes to master the use of GIS software – it can be a slow and time-consuming process to collect the necessary data, analyze it, produce the maps and the special IT equipment.
GIS software, with its ability to process large amounts of data based on spatial information, makes it easier to handle planning and engineering tasks. Using GIS, it is possible to display an unimaginable amount of data on a single map, for example, the underground installation of an entire city (set of electrical cables, gas pipeline, drainage, sewage). Such maps are important because they are used as guides for construction workers and contractors during execution works. In the competitive world of today, successful management requires the maximum from all available resources, people, equipment and information. Using GIS to integrate geography with other relevant data, we will have a system fully equipped for this task.
For any question be free to contact us!
