Gabion walls
Gabion walls – function, application, advantage
The word „gabion“ comes from an old italian word, gabbione, that means „big cage“. Around 7000 years ago, early gabion type structures protected the bank of river Nile. In middle ages, gabions were used as military forts. In earlier history, civil engineers have extensively used gabions for stabillization of banks, coasts, highways and erosion control of slopes. From the banks of river Nile, where they were created up to today, gabion walls are a benefit for the landscape. It is used for thosands of years as a gravity type retaining structure and makes a attractive, efficient and cheap wall system.
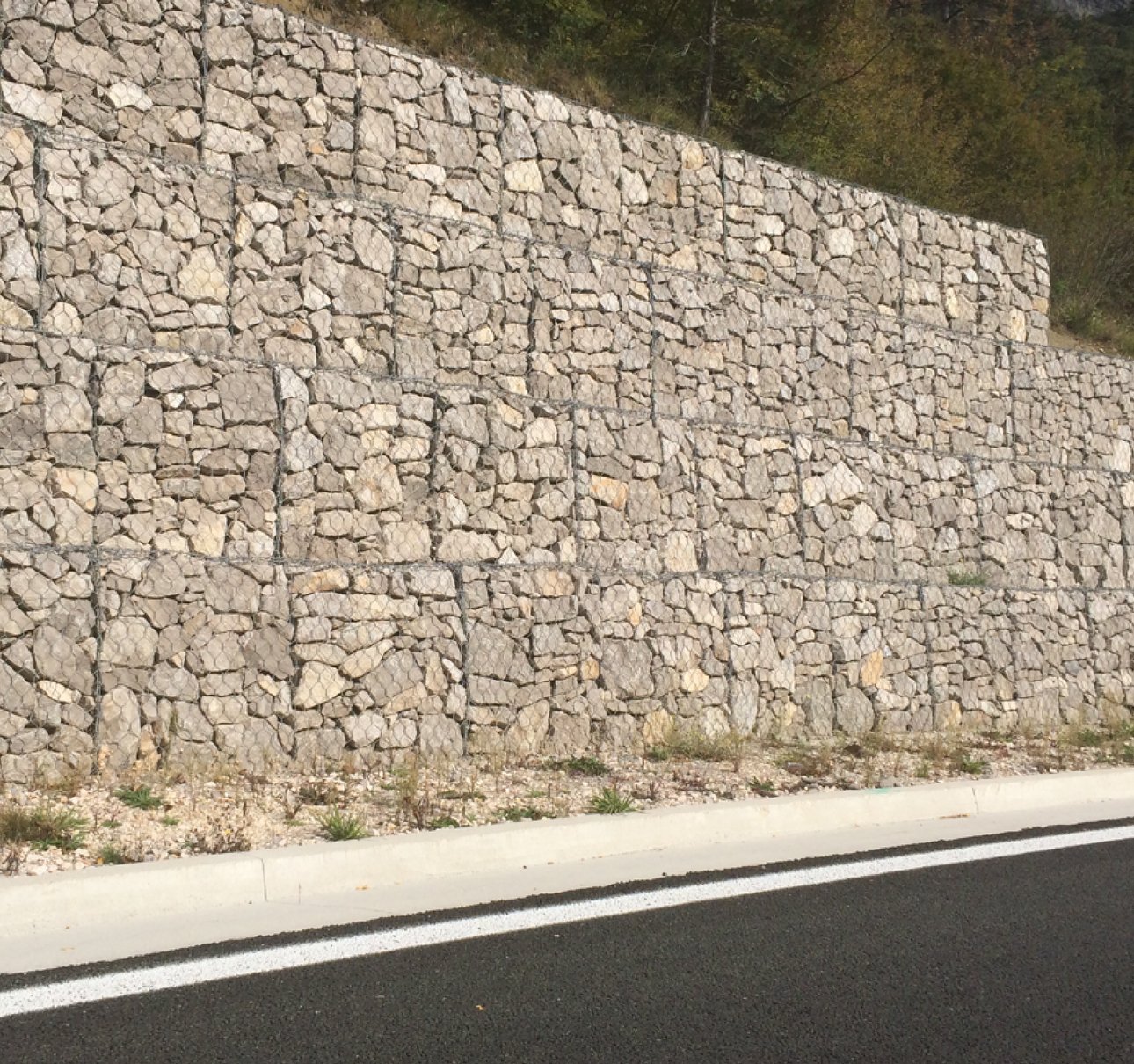
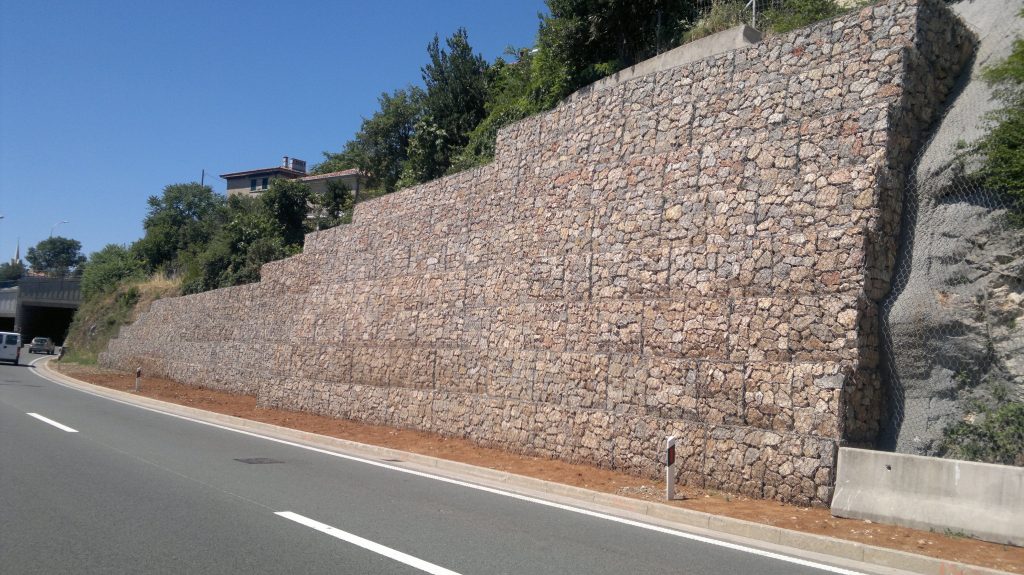
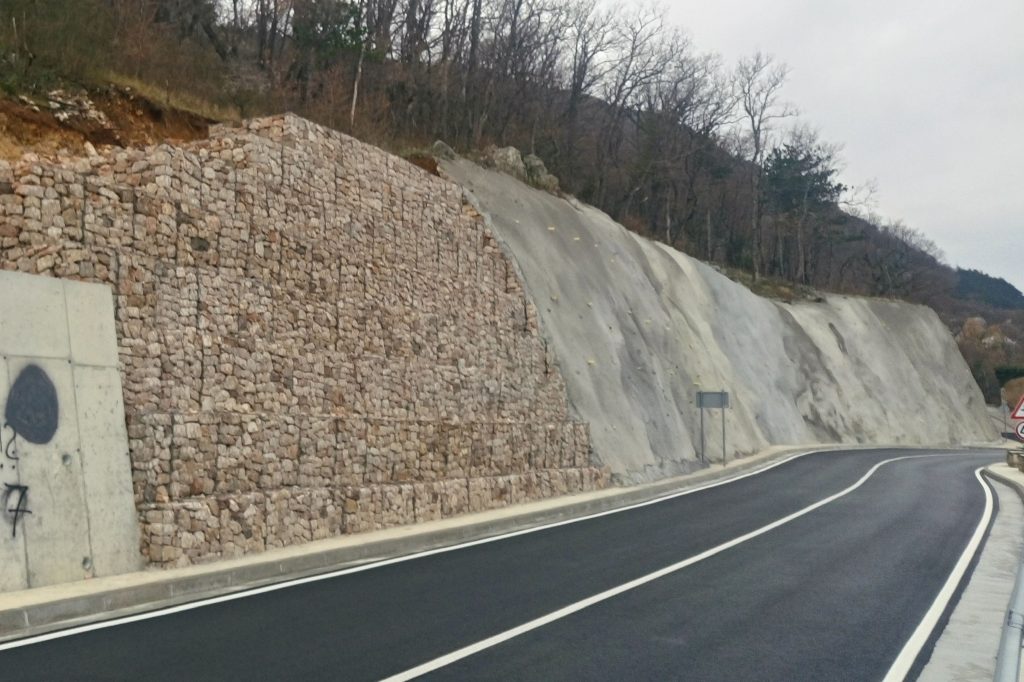
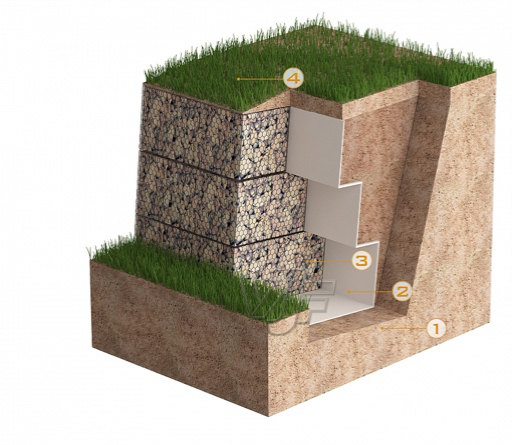
Gabion walls are executed mainly in the purpose of soil stabilization behind the wall, but it can also be executed as a cover wall. The wall si made from gabion baskets that are stacked in one or more rows, depending on the height of the wall. Baskets have a cage shape and are closed on all sides. They are made from a galvanized hexagonal meshes and brocken rock that are placed in the baskets. Retaining structures are formed by stacking gabion baskets in a proper schedule and present an alternative solution for concrete structures in the area of soil stabilization.
Gabion walls have an application mostly in road engineering, e.g. construction of roads, embankments, retaining walls, slope protection, water barriers etc., and can have different functions:
• creation of a barrier that prevents soil erosion in coast and embankment stabilization
• prevention of sliding and washouts
• water speed reduction in prevention of soil erosion in water ways
• noise protection
• aesthetic fence structures for gardens
Benefits of gabion walls:
• Aesthetic – gabion walls look natural and by using natural materials fits into the environment
• Compatibility with the environment – using the material made by excavations the costs of acquisition and transport are significantly reduced
• Is used as a cooling system in hot climate conditions and provides passve cooling by air movement
• Water permeability – gabion walls are permeable and are not damaged by passing water
• Efficiency of gabion walls can increase in time, since the vegetation fills voids and strengthens the wall structure
• Soil movements don’t negatively influence gabion walls, which is an advantage in regard to stiffer structures (reinforced concrete walls)
• Longevity – stone blocks are materials that are frequently used beacuse of their longevity, durability and stability. Usually the stone is selected beacuse of aesthetic attributes or the possibility of excavation produced material usage.
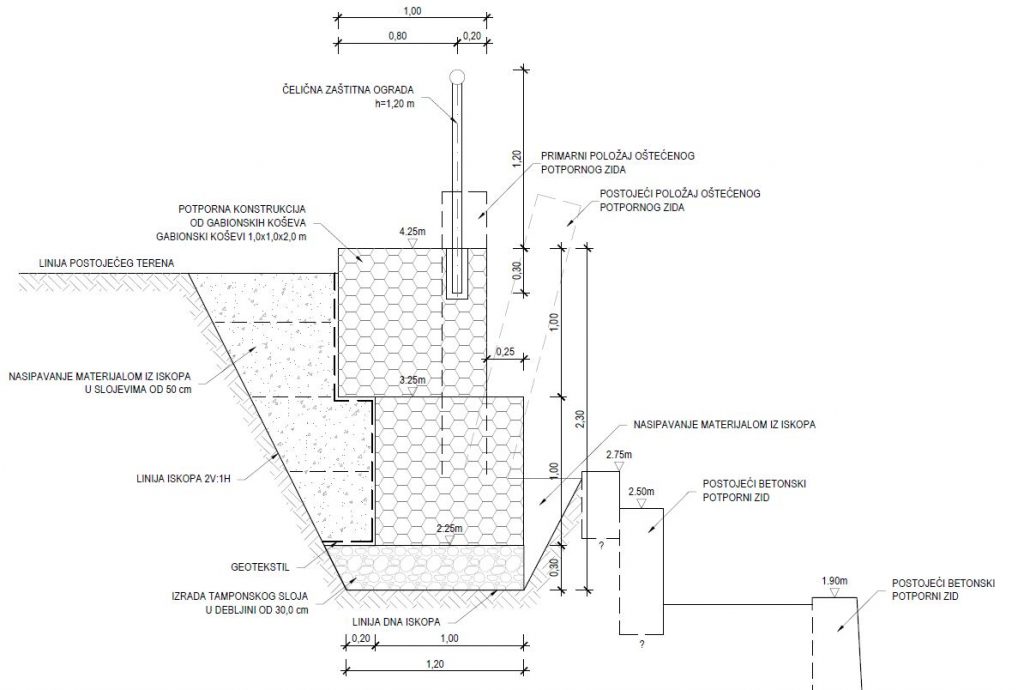
Common gabion basket dimensions are 2,0 x 1,0 x 1,0 m. Galvanized mesh has a hexagonal shape with the eye size X x Y = 8,0 x 10,0 cm.
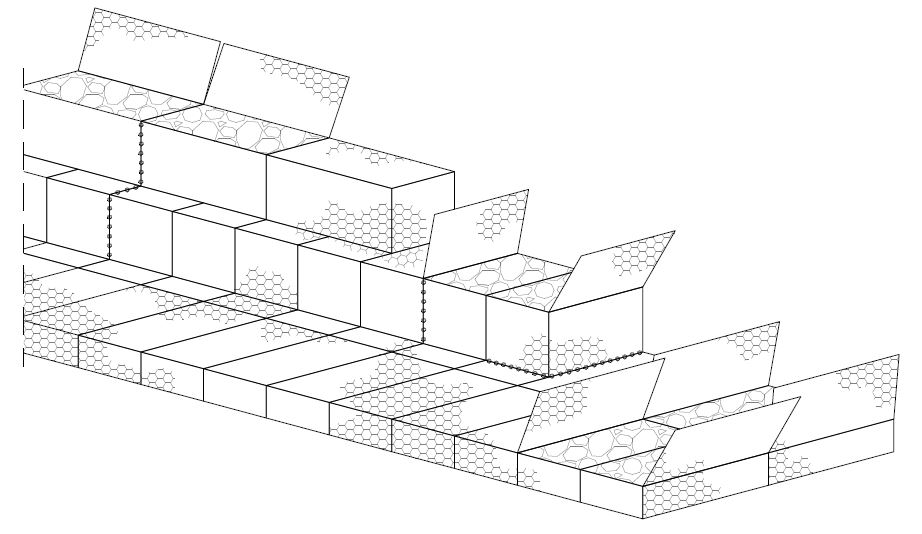
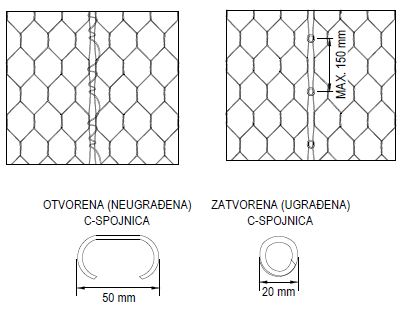
After the baskets are stacked they are connected with galvanized wire to prevent deformation under the weight of upper gabion rows.
Brocken rocks that are used as a fill have to be from natural stone resistant to atmosferic influence. Rocks are placed in the vicinity of gabion baskets and are machine or hand placed. After filling, baskets are closed and connections on meshes are attached with galvanized steel rings.
Gabion baskets are folded when transported to the construction site in order to take up as little as space as possible. After transport, baskets are unfolded, connected and prepared for positioning.
First row of gabion baskets is placed on a foundation made from stone material or concrete, depending on project requirements. The second row is placed on a way that it is moved from the outer edge toward the back in a certain distance. After completing the basket, the space behind the basket is filled with a suitable material up to the height of the upper gabion row.
On the back face, geotextile is placed in order to seperate fine particles from the stone material of the gabion wall. With this the water permeability and filtration mechanism that limits washout is secured.